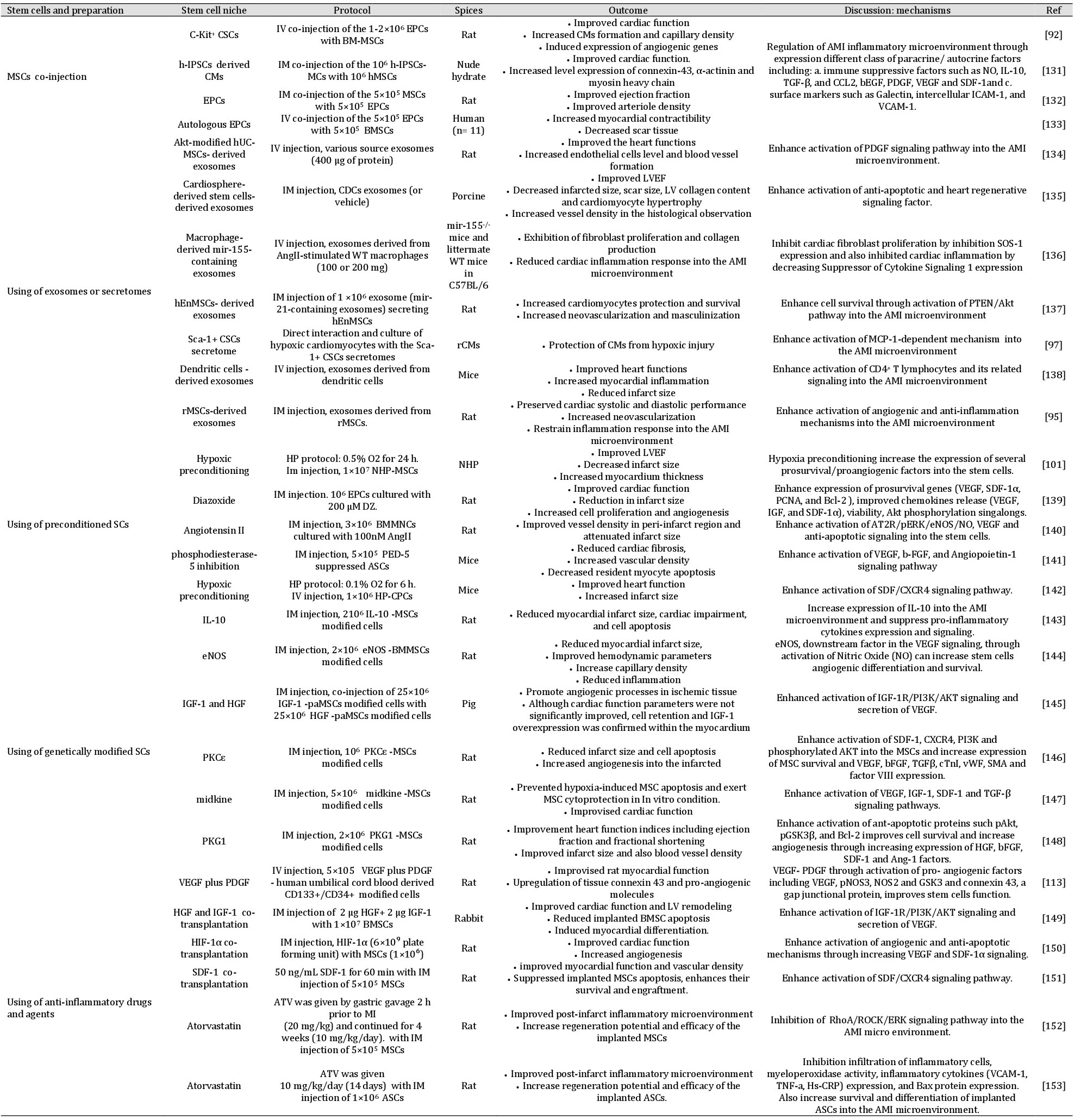
Table 2. Main stem cell therapy studies showing more improvement in AMI due to MSCs co-injection, SCs exosomes/ secretomes synchronic administration, and preconditioned or gene modified SCs. Keys: ASCs: adipose tissue derived-stem cell, AT2R/p-ERK/eNOS/NO: angiotensin type 2 receptor / extracellular-signal-regulated kinase/ endothelial nitric oxide/ nitric oxide, Bax: Bcl-2-associated X protein, Bcl2: B-cell lymphoma 2, bEGF: human epidermal growth factor, CCL2: C-C motif chemokine ligand 2, CMs: cardiomyocytes, cTnI: although assays for cardiac troponin T, eNOS: endothelial Nitric Oxide, hEnMSCs: human endometrium mesenchymal stem cells, HIF-1α: hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, hIPSCs: human inductive pluripotent stem cell, Hs-CRP: High-sensitivity CRP, hUC-MSCs: human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells, ICAM-1: Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1, IL-10: interloukin-10, IM injection: Intramyocardial injection, IV injection: Intravein injection, LV: left ventricle, LVEF: left ventricular injection fraction, NO: nitric oxide, PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen, PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor, pGSK3β: phospho Glycogen synthase kinase 3 β, PKCɛ: protein kinase C ɛ, PKG1: protein kinase G1, PTEN/Akt: phosphatase and tensin homolog/ Protein kinase B, RhoA/ROCK/ERK: Ras homolog gene family, member A/ Rho-associated protein kinase/ extracellular signal-regulated kinases, rMSCs: rat mesenchymal stem cells, SDF/CXCR4: stem cell derived factor/ C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4, SDF-1: stem cell derived growth factor-1, SMA: smooth muscle actin, SOS-1: Son of sevenless homolog 1, TGF-β: Tumor necrosis factor- β, TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor- α,, VCAM-1: Vascular cell adhesion protein 1, VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor, and vWF: von willebrand factor